Management of NCD
Overview
Noncommunicable disease (NCD) management is critical to achieving the global target of a 25% reduction in premature mortality by 2025 and the SDG goal of a one-third reduction by 2030. As of 2021, 9.5 million people died of noncommunicable diseases (males 4.7 million; females 4.8 million).
NCD management includes screening, detection and treatment of the diseases, as well as palliative care for those in need.
NCD management interventions are critical for achieving the global target of a 25% relative reduction in the risk of premature mortality from NCDs by 2025, and the SDG target of a one-third reduction in premature deaths from NCDs by 2030. The Objective 4 of Global action plan for prevention and control of NCDs 2013-2030 seeks to “strengthen and orient health systems to address the prevention and control of NCDs and the underlying social determinants through people-centred primary health care and universal health coverage”. Effective NCD control, aligned with Universal Health Coverage, requires accessible and affordable services, evidence-based guidelines, essential medicines, trained health workers, and robust information systems at the primary health care level.
The WHO South-East Asia Regional Strategy for comprehensive cancer prevention and management 2024–2030, approved by the Seventy-seventh session of Regional Committee is developed to serve as a guide to promote a contextualized, evidence-based approach to cancer control, leveraging support from the global initiatives on cancer.
WHO South-East Asia Response
WHO SE Asia Regional Office works with Member States and partners to improve NCD care services as a public health priority. Implementation roadmap for accelerating the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases in South-East Asia 2022-2030 provides strategic directions and tools with a view to prioritizing and accelerating high-impact interventions that are feasible within the national context. It provides guidance for prevention and control of NCDs, including links and tools for easy access. homev2 | WHO South-East Asia Regional NCD Roadmap
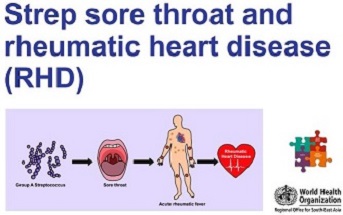
The Seventy-sixth session of WHO SE Asia Regional Committee in 2023 adopted the Resolution on ‘SEAHEARTS: Accelerating prevention and control of cardiovascular diseases in the South-East Asia Region (SEA/RC76/R5)’ . The resolution aims to accelerate the national responses with time-bound commitments to improve treatment coverage of hypertension and diabetes in primary health care along with reduction of risk factors.
Key facts
- Hypertension is leading attributable risk factor for NCDs in the region. Every 1 in 3 adults is suffering from hypertension in the region. High systolic blood pressure is responsible for 2.4 million deaths in the region (around 25% of all global deaths due to high systolic blood pressure).
- Prevalence of hypertension among adults aged 30–79 is estimated to be above 32.57% indicating more than 294 million people with hypertension in the region in 2019
- The hypertension care case cascade indicates that more than 61% are undiagnosed, and only 29% are on treatment and less than 14% have controlled status among hypertensive population in the region
- Over 276 million adults aged 18 years and above are suffering from diabetes in WHO SE Asia Region as per 2022 Global Health estimates.
- Alarmingly, more than 50% of people with diabetes are unaware of their condition, and it is estimated that over 177 million individuals living with diabetes in the region are not receiving treatment
- In 2021, chronic respiratory diseases caused approximately 1.56 million deaths in the region, with COPD accounting for nearly 1.24 million and asthma for 254,834 deaths. Approximately 37% of these deaths occurred before the age of 70.
- The prevalence of chronic respiratory diseases for the SE Asia Region as 4.73% affecting over 104 million individuals
- WHO Package of essential noncommunicable (PEN) disease interventions for primary health care is a framework for strengthening the equity and efficiency of primary health care in low-resource settings for the integrated management of NCDs.
- The HEARTS technical package provides a strategic approach to improving cardiovascular health in countries in primary care settings.